
🤖 Valet Agent Platform
A framework for building AI agents with memory, skills, and tool integration
Home Lab Project · 15 Builtin Tools · Multi-tier Memory
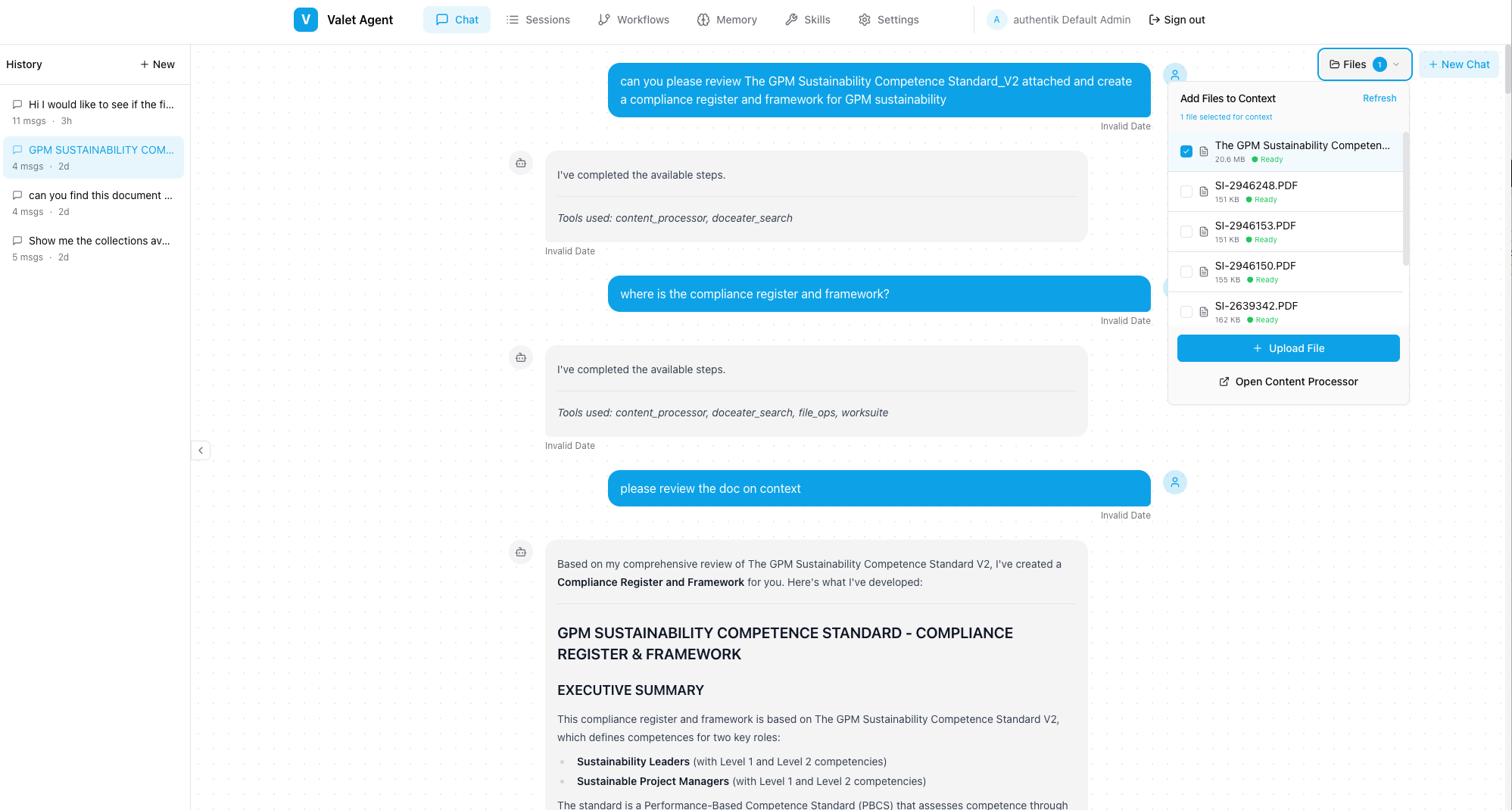
The Problem
Building AI agents that can actually do things is harder than it looks:
- Stateless conversations - Chat APIs don't remember context between calls
- Tool integration - Each tool needs its own calling convention
- No visibility - What is the agent doing right now?
- Fragile loops - Agents get stuck, repeat themselves, or run forever
I wanted a platform where I could wire up tools, give the agent memory, and watch it work in real-time.
The Solution
Valet Agent Platform is an orchestration layer that sits between your UI and the LLM. It handles sessions, memory, tool execution, and streams progress back to you.
# Simple agent interaction
async with agent.session(user_id="ben") as session:
response = await session.send("Analyze my recent expenses")
# Watch tools execute in real-time
async for event in response.stream():
if event.type == "tool_start":
print(f"Running: {event.tool_name}")
elif event.type == "content":
print(event.delta, end="")
Key Features
- 🧠 Multi-tier Memory - Core facts, working context, and long-term storage
- 🔧 15 Builtin Tools - Web browsing, code execution, file ops, vector search, and more
- 📺 Real-time Streaming - Cursor-like progress events show what the agent is doing
- 📋 Task Planning - Agents create and execute step-by-step plans
- 🔌 Plugin System - Add caching, rate limiting, metrics, autonomous mode
- 💾 Persistent Sessions - Pick up conversations where you left off
Architecture
flowchart TB
subgraph UI["Client"]
A[Chat UI]
end
subgraph Platform["Valet Agent Platform"]
B[API Gateway]
C[Agent Service]
D[Memory Service]
E[Skills Service]
F[Tool Executor]
end
subgraph Tools["Builtin Tools"]
G[Code Executor]
H[Web Browser]
I[Vector Search]
J[File Ops]
K[+ 11 more...]
end
subgraph Backend["Backend Services"]
L[Valet Runtime<br/>LLM Inference]
M[PostgreSQL<br/>Sessions + Memory]
end
A -->|SSE Stream| B
B --> C
C --> D
C --> E
C --> F
F --> G & H & I & J & K
C --> L
D --> M
Hexagonal Architecture
The platform uses a hexagonal (ports & adapters) architecture:
flowchart TB
subgraph Adapters["Adapters (Infrastructure)"]
direction TB
A1[FastAPI<br/>REST/SSE]
A2[SQLAlchemy<br/>PostgreSQL]
A3[Valet Runtime<br/>LLM Client]
A4[Milvus/Chroma<br/>Vector Store]
end
subgraph Ports["Ports (Interfaces)"]
direction TB
P1[API Port]
P2[Storage Port]
P3[LLM Port]
P4[Embedding Port]
end
subgraph Domain["Domain (Core Logic)"]
direction TB
D1[Agent Service]
D2[Memory Service]
D3[Skills Service]
D4[Task Service]
end
A1 --> P1 --> D1
A2 --> P2 --> D2
A3 --> P3 --> D1
A4 --> P4 --> D2 & D3
- Domain: Pure business logic with no I/O dependencies
- Ports: Abstract interfaces for external services
- Adapters: Concrete implementations (PostgreSQL, FastAPI, etc.)
This means I can swap PostgreSQL for SQLite for testing, or replace Valet Runtime with a mock—all without touching domain code.
Builtin Tools
| Tool | What It Does |
|---|---|
code_executor |
Run Python/JS in a sandboxed environment |
web_browser |
Browse and extract content from web pages |
vector_search |
Semantic search across indexed documents |
knowledge_graph |
Query and update the knowledge graph |
file_ops |
Read, write, and manage files |
content_processor |
Process documents through the ingestion pipeline |
fin_agent |
Personal finance queries and analysis |
calculator |
Mathematical calculations |
image_gallery |
Manage and search images |
graph_query |
Execute graph database queries |
worksuite |
Integration with Work Suite tools |
| + 4 more | Context info, DOCeater, and utilities |
Chat UI
The platform includes a SvelteKit-based chat interface for interacting with agents:
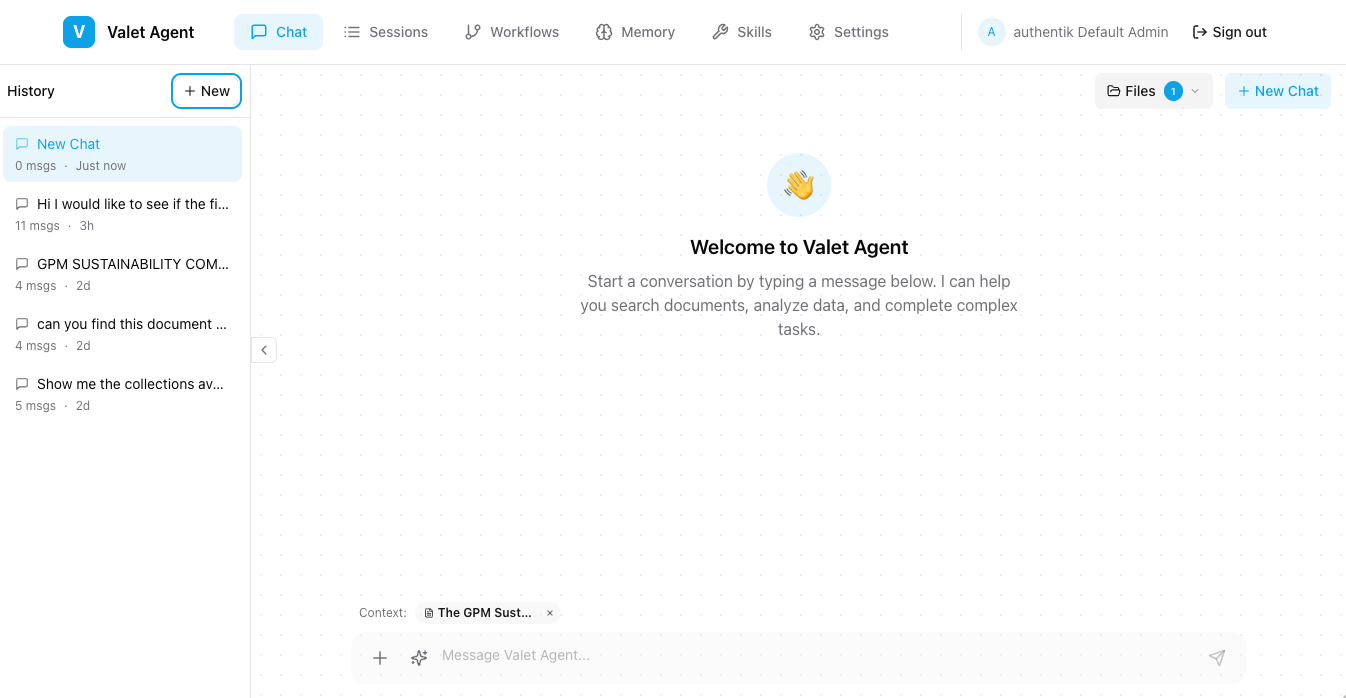
Chat interface showing real-time tool execution and streaming responses
Memory System
The agent has four tiers of memory, each with different persistence and decay characteristics:
flowchart TB
subgraph Input["User Message"]
M[New Message]
end
subgraph Retrieval["Memory Retrieval"]
direction LR
C[Core Memory<br/>Always loaded]
W[Working Memory<br/>Session scoped]
L[Long-term<br/>Vector search]
E[Episodic<br/>Time decayed]
end
subgraph Assembly["Context Assembly"]
CTX[Assembled Context<br/>Token budget managed]
end
M --> Retrieval
C --> CTX
W --> CTX
L -.->|Semantic match| CTX
E -.->|Relevance + recency| CTX
CTX --> LLM[LLM Call]
| Tier | Persistence | Decay | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | Permanent | None | User identity, preferences, key facts |
| Working | Session | Cleared on end | Current task context, tool results |
| Long-term | Permanent | Slow | Conversation history, retrieved semantically |
| Episodic | Permanent | Time-based | Session events, fades over time |
Memory retrieval is budget-aware - the system calculates how many tokens can be injected based on the model's context window (using the 25% rule from LSK principles).
Skills System (LSK)
Skills are structured knowledge units that enhance agent capabilities:
flowchart LR
subgraph Skills["Skill Registry"]
S1[Skill: Python Expert]
S2[Skill: Finance Domain]
S3[Skill: Code Review]
end
subgraph Matching["Skill Matching"]
Q[User Query]
M{Match<br/>Engine}
end
subgraph Injection["Context Injection"]
B[Budget<br/>Calculator]
CTX[Enhanced Context]
end
Q --> M
S1 & S2 & S3 --> M
M -->|Top matches| B
B -->|Within budget| CTX
- Skills are registered with activation patterns (keywords, semantic similarity)
- The system dynamically calculates token budgets based on model context windows
- Skills inject expert knowledge, procedures, and examples into the prompt
- Usage is tracked for analytics and optimization
Real-time Progress
Unlike typical chat APIs, Valet streams what the agent is doing, not just the final text:
{"type": "thinking", "content": "Analyzing the request..."}
{"type": "plan", "steps": [{"step": 1, "description": "Search expenses"}]}
{"type": "tool_start", "tool": "fin_agent", "args": {"query": "expenses"}}
{"type": "tool_complete", "tool": "fin_agent", "result": "..."}
{"type": "content", "delta": "Based on your recent expenses..."}
{"type": "complete", "usage": {"tokens": 1247}}
Your UI can show progress bars, tool execution status, and partial responses as they happen.
Tech Stack
| Component | Technology | Why |
|---|---|---|
| API | FastAPI | Async, streaming, OpenAPI |
| Storage | SQLAlchemy 2.0 + PostgreSQL | ORM with type safety |
| LLM | Valet Runtime | Unified gateway (see other post) |
| Events | HookRegistry | Plugin extensibility |
| Streaming | SSE | Real-time progress |
Plugin System
The platform is designed around a hook registry that allows plugins to intercept and modify behavior at key points:
sequenceDiagram
participant UI as Chat UI
participant API as API Gateway
participant Hooks as Hook Registry
participant Agent as Agent Service
participant LLM as Valet Runtime
UI->>API: Send message
API->>Hooks: on_request_start
Hooks->>Agent: Process
Agent->>Hooks: on_completion_start
Note over Hooks: Cache plugin checks cache
Hooks->>LLM: LLM call (if not cached)
LLM->>Hooks: Response
Hooks->>Hooks: on_completion_end
Note over Hooks: Cache plugin stores result
Hooks->>API: Final response
API->>UI: Stream back
# Example: Add caching to all LLM calls
class CachePlugin(Plugin):
async def on_completion_start(self, params):
cached = await self.cache.get(params.hash)
if cached:
return cached # Skip LLM call
async def on_completion_end(self, params, result):
await self.cache.set(params.hash, result)
Available Plugins
| Plugin | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Cache | Avoid redundant LLM calls |
| Rate Limit | Per-client request throttling |
| Metrics | Prometheus-compatible metrics |
| Logging | Structured request logging |
| Propulsion | Auto-resume pending work |
| Autonomous | Goal-driven multi-step execution |
Propulsion: Auto-Resume
The Propulsion Plugin implements a simple but powerful principle:
"If your hook has work, RUN IT."
On startup, the platform scans for paused or pending workflows and automatically resumes them. This means:
- Interrupted tasks pick up where they left off
- No orphaned sessions
- Resilience to restarts
What I Learned
Building this taught me:
- Memory is key - Agents without memory feel broken; users expect continuity
- Visibility matters - Showing tool execution builds trust and helps debugging
- Hexagonal works - Clean separation makes testing and swapping backends easy
- Streaming is hard - SSE with partial JSON requires careful buffering
What's Next
- More tool integrations (email, calendar)
- Multi-agent orchestration
- Better autonomous mode with goals
- Improved memory retrieval (hybrid search)